



|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

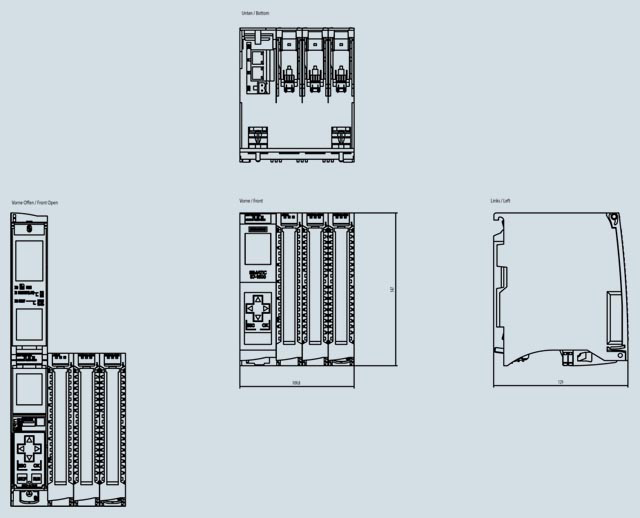
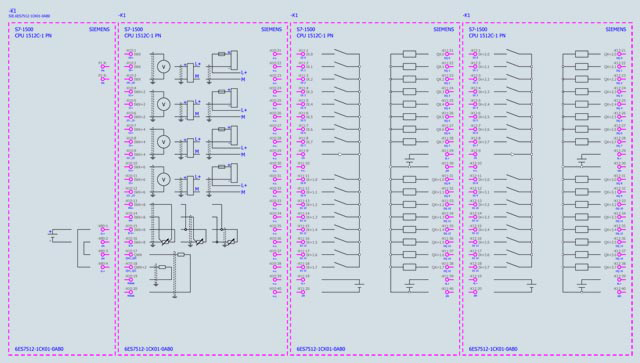
| General information | ||
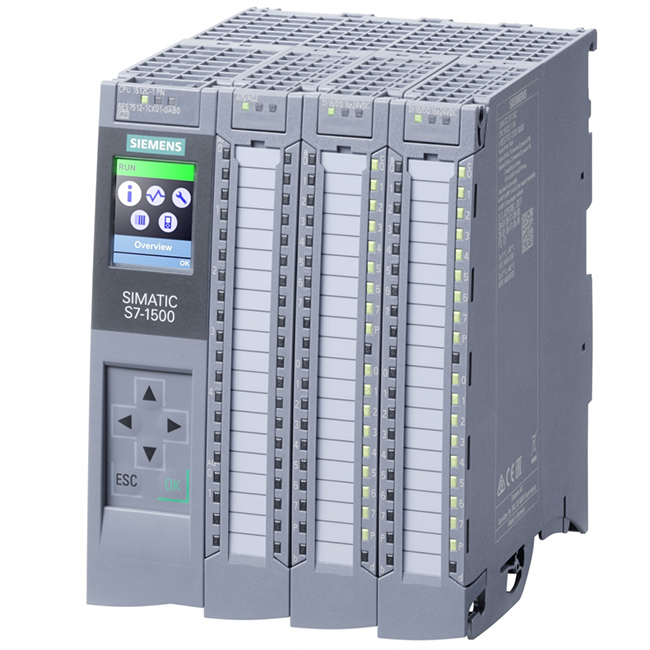
| Product type designation | CPU 1512C-1 PN | |
| HW functional status | FS01 | |
| Firmware version | V2.6 | |
| Product function | ||
| ● I&M data | Yes; I&M0 to I&M3 | |
| Engineering with | ||
| ● STEP 7 TIA Portal configurable/integrated as of version | V15.1 (FW V2.6) / V15 (FW V2.5) or higher; with older TIA Portal versions configurable as 6ES7512-1CK00-0AB0 | |
| Configuration control | ||
| via dataset | Yes | |
| Display | ||
| Screen diagonal [cm] | 3.45 cm | |
| Control elements | ||
| Number of keys | 8 | |
| Mode buttons | 2 | |
| Supply voltage | ||
| Type of supply voltage | 24 V DC | |
| permissible range, lower limit (DC) | 19.2 V; 20.4 V DC, for supplying the digital inputs/outputs | |
| permissible range, upper limit (DC) | 28.8 V | |
| Reverse polarity protection | Yes | |
| Mains buffering | ||
| ● Mains/voltage failure stored energy time | 5 ms; Refers to the power supply on the CPU section | |
| ● Repeat rate, min. | 1/s | |
| Input current | ||
| Current consumption (rated value) | 0.8 A; Without load; 18.8 A: CPU + load | |
| Current consumption, max. | 1 A; Without load; 19 A: CPU + load | |
| Inrush current, max. | 1.9 A; Rated value | |
| I²t | 0.34 A²·s | |
| Digital inputs | ||
| ● from load voltage L+ (without load), max. | 20 mA; per group | |
| Digital outputs | ||
| ● from load voltage L+, max. | 30 mA; Per group, without load | |
| Output voltage | ||
| Rated value (DC) | 24 V | |
| Encoder supply | ||
| Number of outputs | 2; One common 24 V encoder supply per 16 digital inputs | |
| 24 V encoder supply | ||
| ● 24 V | Yes; L+ (-0.8 V) | |
| ● Short-circuit protection | Yes | |
| ● Output current, max. | 1 A | |
| Power | ||
| Infeed power to the backplane bus | 10 W | |
| Power consumption from the backplane bus (balanced) | 9 W | |
| Power loss | ||
| Power loss, typ. | 15.2 W | |
| Memory | ||
| Number of slots for SIMATIC memory card | 1 | |
| SIMATIC memory card required | Yes | |
| Work memory | ||
| ● integrated (for program) | 250 kbyte | |
| ● integrated (for data) | 1 Mbyte | |
| Load memory | ||
| ● Plug-in (SIMATIC Memory Card), max. | 32 Gbyte | |
| Backup | ||
| ● maintenance-free | Yes | |
| CPU processing times | ||
| for bit operations, typ. | 48 ns | |
| for word operations, typ. | 58 ns | |
| for fixed point arithmetic, typ. | 77 ns | |
| for floating point arithmetic, typ. | 307 ns | |
| CPU-blocks | ||
| Number of elements (total) | 2 000; Blocks (OB, FB, FC, DB) and UDTs | |
| DB | ||
| ● Number range | 1 ... 60 999; subdivided into: number range that can be used by the user: 1 ... 59 999, and number range of DBs created via SFC 86: 60 000 ... 60 999 | |
| ● Size, max. | 1 Mbyte; For DBs with absolute addressing, the max. size is 64 KB | |
| FB | ||
| ● Number range | 0 ... 65 535 | |
| ● Size, max. | 250 kbyte | |
| FC | ||
| ● Number range | 0 ... 65 535 | |
| ● Size, max. | 250 kbyte | |
| OB | ||
| ● Size, max. | 250 kbyte | |
| ● Number of free cycle OBs | 100 | |
| ● Number of time alarm OBs | 20 | |
| ● Number of delay alarm OBs | 20 | |
| ● Number of cyclic interrupt OBs | 20; With minimum OB 3x cycle of 500 µs | |
| ● Number of process alarm OBs | 50 | |
| ● Number of DPV1 alarm OBs | 3 | |
| ● Number of isochronous mode OBs | 1 | |
| ● Number of technology synchronous alarm OBs | 2 | |
| ● Number of startup OBs | 100 | |
| ● Number of asynchronous error OBs | 4 | |
| ● Number of synchronous error OBs | 2 | |
| ● Number of diagnostic alarm OBs | 1 | |
| Nesting depth | ||
| ● per priority class | 24 | |
| Counters, timers and their retentivity | ||
| S7 counter | ||
| ● Number | 2 048 | |
| Retentivity | ||
| — adjustable | Yes | |
| IEC counter | ||
| ● Number | Any (only limited by the main memory) | |
| Retentivity | ||
| — adjustable | Yes | |
| S7 times | ||
| ● Number | 2 048 | |
| Retentivity | ||
| — adjustable | Yes | |
| IEC timer | ||
| ● Number | Any (only limited by the main memory) | |
| Retentivity | ||
| — adjustable | Yes | |
| Data areas and their retentivity | ||
| Retentive data area (incl. timers, counters, flags), max. | 128 kbyte; In total; available retentive memory for bit memories, timers, counters, DBs, and technology data (axes): 88 KB | |
| Extended retentive data area (incl. timers, counters, flags), max. | 1 Mbyte; When using PS 6 0W 24/48/60 V DC HF | |
| Flag | ||
| ● Number, max. | 16 kbyte | |
| ● Number of clock memories | 8; 8 clock memory bit, grouped into one clock memory byte | |
| Data blocks | ||
| ● Retentivity adjustable | Yes | |
| ● Retentivity preset | No | |
| Local data | ||
| ● per priority class, max. | 64 kbyte; max. 16 KB per block | |
| Address area | ||
| Number of IO modules | 2 048; max. number of modules / submodules | |
| I/O address area | ||
| ● Inputs | 32 kbyte; All inputs are in the process image | |
| ● Outputs | 32 kbyte; All outputs are in the process image | |
| per integrated IO subsystem | ||
| — Inputs (volume) | 8 kbyte | |
| — Outputs (volume) | 8 kbyte | |
| per CM/CP | ||
| — Inputs (volume) | 8 kbyte | |
| — Outputs (volume) | 8 kbyte | |
| Subprocess images | ||
| ● Number of subprocess images, max. | 32 | |
| Hardware configuration | ||
| Number of distributed IO systems | 32; A distributed I/O system is characterized not only by the integration of distributed I/O via PROFINET or PROFIBUS communication modules, but also by the connection of I/O via AS-i master modules or links (e.g. IE/PB-Link) | |
| Number of DP masters | ||
| ● Via CM | 6; A maximum of 6 CMs/CPs (PROFIBUS, PROFINET, Ethernet) can be inserted in total | |
| Number of IO Controllers | ||
| ● integrated | 1 | |
| ● Via CM | 6; A maximum of 6 CMs/CPs (PROFIBUS, PROFINET, Ethernet) can be inserted in total | |
| Rack | ||
| ● Modules per rack, max. | 32; CPU + 31 modules | |
| ● Number of lines, max. | 1 | |
| PtP CM | ||
| ● Number of PtP CMs | the number of connectable PtP CMs is only limited by the number of available slots | |
| Time of day | ||
| Clock | ||
| ● Type | Hardware clock | |
| ● Backup time | 6 wk; At 40 °C ambient temperature, typically | |
| ● Deviation per day, max. | 10 s; Typ.: 2 s | |
| Operating hours counter | ||
| ● Number | 16 | |
| Clock synchronization | ||
| ● supported | Yes | |
| ● in AS, master | Yes | |
| ● in AS, slave | Yes | |
| ● on Ethernet via NTP | Yes | |
| Digital inputs | ||
| integrated channels (DI) | 32 | |
| Digital inputs, parameterizable | Yes | |
| Source/sink input | P-reading | |
| Input characteristic curve in accordance with IEC 61131, type 3 | Yes | |
| Digital input functions, parameterizable | ||
| ● Gate start/stop | Yes | |
| ● Capture | Yes | |
| ● Synchronization | Yes | |
| Input voltage | ||
| ● Type of input voltage | DC | |
| ● Rated value (DC) | 24 V | |
| ● for signal "0" | -3 to +5V | |
| ● for signal "1" | +11 to +30V | |
| Input current | ||
| ● for signal "1", typ. | 2.5 mA | |
| Input delay (for rated value of input voltage) | ||
| for standard inputs | ||
| — parameterizable | Yes; none / 0.05 / 0.1 / 0.4 / 1.6 / 3.2 / 12.8 / 20 ms | |
| — at "0" to "1", min. | 4 µs; for parameterization "none" | |
| — at "0" to "1", max. | 20 ms | |
| — at "1" to "0", min. | 4 µs; for parameterization "none" | |
| — at "1" to "0", max. | 20 ms | |
| for interrupt inputs | ||
| — parameterizable | Yes; Same as for standard inputs | |
| for technological functions | ||
| — parameterizable | Yes; Same as for standard inputs | |
| Cable length | ||
| ● shielded, max. | 1 000 m; 600 m for technological functions; depending on input frequency, encoder and cable quality; max. 50 m at 100 kHz | |
| ● unshielded, max. | 600 m; For technological functions: No | |
| Digital outputs | ||
| Type of digital output | Transistor | |
| integrated channels (DO) | 32 | |
| Current-sourcing | Yes; Push-pull output | |
| Short-circuit protection | Yes; electronic/thermal | |
| ● Response threshold, typ. | 1.6 A with standard output, 0.5 A with high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| Limitation of inductive shutdown voltage to | Connector X11: -0.8 V; connector X12: L+ (-53 V) | |
| Controlling a digital input | Yes | |
| Accuracy of pulse duration | Up to ±100 ppm ±2 μs at high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| minimum pulse duration | 2 µs; With High Speed output | |
| Digital output functions, parameterizable | ||
| ● Switching tripped by comparison values | Yes; As output signal of a high-speed counter | |
| ● PWM output | Yes | |
| — Number, max. | 4 | |
| — Cycle duration, parameterizable | Yes | |
| — ON period, min. | 0 % | |
| — ON period, max. | 100 % | |
| — Resolution of the duty cycle | 0.0036 %; For S7 analog format, min. 40 ns | |
| ● Frequency output | Yes | |
| ● Pulse train | Yes; also for pulse/direction interface | |
| Switching capacity of the outputs | ||
| ● with resistive load, max. | 0.5 A; 0.1 A with high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| ● on lamp load, max. | 5 W; 1 W with high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| Load resistance range | ||
| ● lower limit | 48 Ω; 240 ohms with high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| ● upper limit | 12 kΩ | |
| Output voltage | ||
| ● Type of output voltage | DC | |
| ● for signal "0", max. | 1 V; With high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output; see manual for details | |
| ● for signal "1", min. | 23.2 V; L+ (-0.8 V) | |
| Output current | ||
| ● for signal "1" rated value | 0.5 A; 0.1 A with high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output, observe derating; see manual for details | |
| ● for signal "1" permissible range, min. | 2 mA | |
| ● for signal "1" permissible range, max. | 0.6 A; 0.12 A with high-speed output, i.e. when using a high-speed output, observe derating; see manual for details | |
| ● for signal "0" residual current, max. | 0.5 mA | |
| Output delay with resistive load | ||
| ● "0" to "1", max. | 200 µs | |
| ● "1" to "0", max. | 500 µs; Load-dependent | |
| for technological functions | ||
| — "0" to "1", max. | 5 µs; Depending on the output used, see additional description in manual | |
| — "1" to "0", max. | 5 µs; Depending on the output used, see additional description in manual | |
| Parallel switching of two outputs | ||
| ● for logic links | Yes; For technological functions: No | |
| ● for uprating | No | |
| ● for redundant control of a load | Yes; For technological functions: No | |
| Switching frequency | ||
| ● with resistive load, max. | 100 kHz; For high-speed output, 100 Hz for standard output | |
| ● with inductive load, max. | 0.5 Hz; Acc. to IEC 60947-5-1, DC-13; observe derating curve | |
| ● on lamp load, max. | 10 Hz | |
| Total current of the outputs | ||
| ● Current per channel, max. | 0.5 A; see additional description in the manual | |
| ● Current per group, max. | 8 A; see additional description in the manual | |
| ● Current per power supply, max. | 4 A; 2 power supplies for each group, current per power supply max. 4 A, see additional description in manual | |
| for technological functions | ||
| — Current per channel, max. | 0.5 A; see additional description in the manual | |
| Relay outputs | ||
| ● Number of relay outputs | 0 | |
| Cable length | ||
| ● shielded, max. | 1 000 m; 600 m for technological functions; depending on output frequency, load, and cable quality; max. 50 m at 100 kHz | |
| ● unshielded, max. | 600 m; For technological functions: No | |
| Analog inputs | ||
| Number of analog inputs | 5; 4x for U/I, 1x for R/RTD | |
| ● For current measurement | 4; max. | |
| ● For voltage measurement | 4; max. | |
| ● For resistance/resistance thermometer measurement | 1 | |
| permissible input voltage for voltage input (destruction limit), max. | 28.8 V | |
| permissible input current for current input (destruction limit), max. | 40 mA | |
| Cycle time (all channels), min. | 1 ms; Dependent on the parameterized interference frequency suppression; for details, see conversion procedure in manual | |
| Technical unit for temperature measurement adjustable | Yes; °C/°F/K | |
| Input ranges (rated values), voltages | ||
| ● 0 to +10 V | Yes; Physical measuring range: ± 10 V | |
| ● Input resistance (0 to 10 V) | 100 kΩ | |
| ● 1 V to 5 V | Yes; Physical measuring range: ± 10 V | |
| ● Input resistance (1 V to 5 V) | 100 kΩ | |
| ● -10 V to +10 V | Yes | |
| ● Input resistance (-10 V to +10 V) | 100 kΩ | |
| ● -5 V to +5 V | Yes; Physical measuring range: ± 10 V | |
| ● Input resistance (-5 V to +5 V) | 100 kΩ | |
| Input ranges (rated values), currents | ||
| ● 0 to 20 mA | Yes; Physical measuring range: ± 20 mA | |
| ● Input resistance (0 to 20 mA) | 50 Ω; Plus approx. 55 ohm for overvoltage protection by PTC | |
| ● -20 mA to +20 mA | Yes | |
| ● Input resistance (-20 mA to +20 mA) | 50 Ω; Plus approx. 55 ohm for overvoltage protection by PTC | |
| ● 4 mA to 20 mA | Yes; Physical measuring range: ± 20 mA | |
| ● Input resistance (4 mA to 20 mA) | 50 Ω; Plus approx. 55 ohm for overvoltage protection by PTC | |
| Input ranges (rated values), resistance thermometer | ||
| ● Ni 100 | Yes; Standard/climate | |
| ● Input resistance (Ni 100) | 10 MΩ | |
| ● Pt 100 | Yes; Standard/climate | |
| ● Input resistance (Pt 100) | 10 MΩ | |
| Input ranges (rated values), resistors | ||
| ● 0 to 150 ohms | Yes; Physical measuring range: 0 ... 600 ohms | |
| ● Input resistance (0 to 150 ohms) | 10 MΩ | |
| ● 0 to 300 ohms | Yes; Physical measuring range: 0 ... 600 ohms | |
| ● Input resistance (0 to 300 ohms) | 10 MΩ | |
| ● 0 to 600 ohms | Yes | |
| ● Input resistance (0 to 600 ohms) | 10 MΩ | |
| Cable length | ||
| ● shielded, max. | 800 m; for U/I, 200 m for R/RTD | |
| Analog outputs | ||
| integrated channels (AO) | 2 | |
| Voltage output, short-circuit protection | Yes | |
| Cycle time (all channels), min. | 1 ms; Dependent on the parameterized interference frequency suppression; for details, see conversion procedure in manual | |
| Output ranges, voltage | ||
| ● 0 to 10 V | Yes | |
| ● 1 V to 5 V | Yes | |
| ● -10 V to +10 V | Yes | |
| Output ranges, current | ||
| ● 0 to 20 mA | Yes | |
| ● -20 mA to +20 mA | Yes | |
| ● 4 mA to 20 mA | Yes | |
| Load impedance (in rated range of output) | ||
| ● with voltage outputs, min. | 1 kΩ | |
| ● with voltage outputs, capacitive load, max. | 100 nF | |
| ● with current outputs, max. | 500 Ω | |
| ● with current outputs, inductive load, max. | 1 mH | |
| Cable length | ||
| ● shielded, max. | 200 m | |
| Analog value generation for the inputs | ||
| Integration and conversion time/resolution per channel | ||
| ● Resolution with overrange (bit including sign), max. | 16 bit | |
| ● Integration time, parameterizable | Yes; 2.5 / 16.67 / 20 / 100 ms, acts on all channels | |
| ● Interference voltage suppression for interference frequency f1 in Hz | 400 / 60 / 50 / 10 | |
| Smoothing of measured values | ||
| ● parameterizable | Yes | |
| ● Step: None | Yes | |
| ● Step: low | Yes | |
| ● Step: Medium | Yes | |
| ● Step: High | Yes | |
| Analog value generation for the outputs | ||
| Integration and conversion time/resolution per channel | ||
| ● Resolution with overrange (bit including sign), max. | 16 bit | |
| Settling time | ||
| ● for resistive load | 1.5 ms | |
| ● for capacitive load | 2.5 ms | |
| ● for inductive load | 2.5 ms | |
| Encoder | ||
| Connection of signal encoders | ||
| ● for voltage measurement | Yes | |
| ● for current measurement as 4-wire transducer | Yes | |
| ● for resistance measurement with two-wire connection | Yes | |
| ● for resistance measurement with three-wire connection | Yes | |
| ● for resistance measurement with four-wire connection | Yes | |
| Connectable encoders | ||
| ● 2-wire sensor | Yes | |
| — permissible quiescent current (2-wire sensor), max. | 1.5 mA | |
| Encoder signals, incremental encoder (asymmetrical) | ||
| ● Input voltage | 24 V | |
| ● Input frequency, max. | 100 kHz | |
| ● Counting frequency, max. | 400 kHz; with quadruple evaluation | |
| ● Signal filter, parameterizable | Yes | |
| ● Incremental encoder with A/B tracks, 90° phase offset | Yes | |
| ● Incremental encoder with A/B tracks, 90° phase offset and zero track | Yes | |
| ● Pulse encoder | Yes | |
| ● Pulse encoder with direction | Yes | |
| ● Pulse encoder with one impulse signal per count direction | Yes | |
| Errors/accuracies | ||
| Linearity error (relative to input range), (+/-) | 0.1 % | |
| Temperature error (relative to input range), (+/-) | 0.005 %/K | |
| Crosstalk between the inputs, max. | -60 dB | |
| Repeat accuracy in steady state at 25 °C (relative to input range), (+/-) | 0.05 % | |
| Output ripple (relative to output range, bandwidth 0 to 50 kHz), (+/-) | 0.02 % | |
| Linearity error (relative to output range), (+/-) | 0.15 % | |
| Temperature error (relative to output range), (+/-) | 0.005 %/K | |
| Crosstalk between the outputs, max. | -80 dB | |
| Repeat accuracy in steady state at 25 °C (relative to output range), (+/-) | 0.05 % | |
| Operational error limit in overall temperature range | ||
| ● Voltage, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.3 % | |
| ● Current, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.3 % | |
| ● Resistance, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.3 % | |
| ● Resistance thermometer, relative to input range, (+/-) | Pt100 Standard: ±2 K, Pt100 Climate: ±1 K, Ni100 Standard: ±1.2 K, Ni100 Climate: ±1 K | |
| ● Voltage, relative to output range, (+/-) | 0.3 % | |
| ● Current, relative to output range, (+/-) | 0.3 % | |
| Basic error limit (operational limit at 25 °C) | ||
| ● Voltage, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.2 % | |
| ● Current, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.2 % | |
| ● Resistance, relative to input range, (+/-) | 0.2 % | |
| ● Resistance thermometer, relative to input range, (+/-) | Pt100 Standard: ±1 K, Pt100 Climate: ±0.5 K, Ni100 Standard: ±0.6 K, Ni100 Climate: ±0.5 K | |
| ● Voltage, relative to output range, (+/-) | 0.2 % | |
| ● Current, relative to output range, (+/-) | 0.2 % | |
| Interference voltage suppression for f = n x (f1 +/- 1 %), f1 = interference frequency | ||
| ● Series mode interference (peak value of interference < rated value of input range), min. | 30 dB | |
| ● Common mode voltage, max. | 10 V | |
| ● Common mode interference, min. | 60 dB; at 400 Hz: 50 dB | |
| Interfaces | ||
| Number of PROFINET interfaces | 1 | |
| 1. Interface | ||
| Interface types | ||
| ● Number of ports | 2 | |
| ● integrated switch | Yes | |
| ● RJ 45 (Ethernet) | Yes; X1 | |
| Protocols | ||
Sản phẩm cùng loại
SẢN PHẨM XEM NHIỀU
 | ||